With the increasing pollution of surface water, traditional water treatment processes have made it difficult to purify water to meet drinking water standards. In recent years, activated carbon filters have received more and more attention as a deep processing unit. After the long-term operation of the activated carbon filter process for treating different water quality, the activated carbon gradually reaches the maximum adsorption capacity, and the adsorption capacity of the filter material deteriorates, and the evaluation of such used filter materials is not perfect. The author adopted the methylene blue standardization test in order to achieve the purpose of scientific evaluation of activated carbon filter materials.
1 Carbon sample preparation and test methods
1•1 activated carbon sample and preparation thereof
Two kinds of activated carbons, such as coal columnar activated carbon and flake activated carbon, were selected for comparison with activated carbon after running for a period of time. The columnar activated carbon and the granular activated carbon have the same texture and production process, and are the crushed charcoal with the same properties; the flake-shaped activated carbon is the shell texture. After operation, the granular activated carbon was taken from the surface water activated carbon filter that has been running continuously for 2 years in the scientific research base of the Yellow River Water Purification Plant of Shandong Water Supply and Drainage Inspection Station. The processing unit has no organic matter penetration, but the influent water quality has little change. In the case, the effluent water quality gradually deteriorates (see Table 1). Due to the different particle sizes of the three activated carbons, in order to facilitate the lateral comparison of the activated carbon, refer to the provisions of the national standard for the activated carbon, the sample is taken out by the quadruple method, and then about 10 g of the sample is ground to pass the zero. The extent of the 042 mm mesh hole, at which point the effect of the selected three activated carbon particle sizes is considered to have been removed.
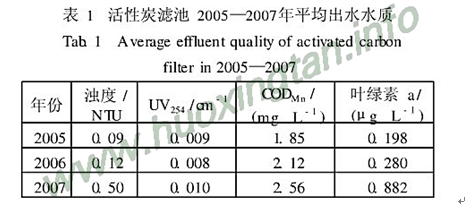
Table 1 Average effluent quality of activated carbon filter from 2005 to 2007
Year turbidity/NTUUV254/cm-1CODMn/(mg•L-1) chlorophyll a/(μg•L-1)
2005 0. 09 0. 009 1. 85 0. 198
2006 0. 12 0. 008 2. 12 0. 280
2007 0. 50 0. 010 2. 56 0. 882
The methylene blue value is the adsorption capacity of activated carbon for adsorbate molecules with a radius of 2 to 100 nm. The higher the methylene blue value, the stronger the adsorption capacity for medium molecules, and the larger the mesopore amount of activated carbon. The singularity of the range is from 1. 6 to 5. 7 nm. Methylene blue molecules have a large linear size at the same time, and theoretically may enter smaller pores, but the possibility of entering large pores is not excluded.
1•2 Test method
A 1.5 mg/mL methylene blue reagent was prepared and the range of methylene blue values ​​of the three carbons was determined [8]. The activated carbon was placed in a volumetric flask, and the desired methylene blue solution was accurately added by a burette, sealed and fixed on a shaker at an oscillation frequency of 120 times/min, and sampled after 1 to 2 hours. After separating the activated carbon from the solution, the concentration of methylene blue in the solution was determined by spectrophotometry and used as the equilibrium concentration of the test, and the Freundlich isotherm was drawn at a point where the unit adsorption amount was within the calculation range. When the equilibrium concentration of the solution reached 0. 000 245 mg/mL, the adsorption of methylene blue reached an optimum value.
2 Freundlich adsorption isotherm test analysis
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm curves of three activated carbons for methylene blue are shown in Fig. 1.
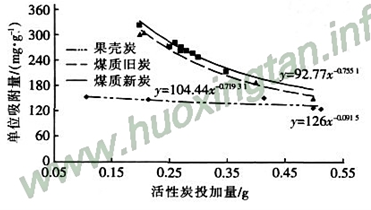
Figure 1 Freundlich adsorption isotherms of three activated carbons
The optimum adsorption capacity of the methylene blue adsorption curve of coal new carbon and coal old carbon corresponding to the equilibrium concentration of 0. 000 245 mg / mL is not much different, respectively, 196. 48 and 185. 65 mg / g, shell charcoal The methylene blue value was 143. 14 mg/g. After the operation for a period of time, the adsorption capacity of activated carbon on organic matter is reduced, but it is not much different from the new carbon. The middle hole and the large hole remain basically in the original state except for a few blockages. After long-term operation, the organic matter has little effect on the structure and adsorption capacity of the medium and large pores of the coal-based activated carbon. The conclusion that the UV254 of the effluent from the filter of the activated carbon is not large also confirms this conclusion. The adsorption strengths of coal new carbon, coal old carbon and shell carbon were 0.069 8, 0. 074 8, 0. 010 88, respectively. After two years of continuous operation, the change of 1/n value of coal-based activated carbon is not obvious, compared with the new carbon, only 7%, still far less than 1, the adsorption rate is ideal, the shell 1/n value is slightly larger than 0.1. The 1/n value is a desirable range in 0.1, and it is clear that the shell carbon adsorption rate is slower. The 1/n value of activated carbon also indicates the concentration of the carbon suitable for the treatment solution. The larger the 1/n value, the more suitable the treatment of high concentration water, and the poor treatment of low concentration water quality is not good. Therefore, coal charcoal is more suitable for the treatment of micro-polluted surface water and drinking water, and can still meet the requirements after long-term operation, while the shell charcoal is more suitable for high-load biofilter. From the degree of fitting of the curve, the data of the shell carbon is not as stable as that of the coal charcoal. After the continuous test of multiple sets of parallel samples, the R values ​​of the shell charcoal, the coal new charcoal and the coal charcoal are 0. 77, 0. 83, 0. 87. This indicates that the shell charcoal is not uniformly activated due to its own texture, and contains more impurities. The coal-based activated carbon has a good treatment effect.
3 Analysis of adsorption phenomena in medium and large pores
Since activated carbon micropores compete for adsorption of the same molecular diameter, in order to study the difference in net adsorption energy of different kinds of activated carbon monomers for the same molecular diameter, the adsorption competition of activated carbon under different adsorption strengths was tested. The final adsorption competition is characterized by the unit adsorption mass at which adsorption equilibrium is reached. The oscillation frequency was 120 times/min, and the equilibrium concentration was measured after 1 hour. The results are shown in Fig. 2.
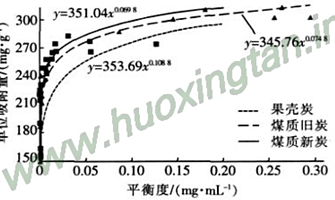
Figure 2 Relationship between methylene blue value and activated carbon quality
It can be seen that under the same test conditions, the unit adsorption amount shows a gradual decrease trend, and the decrease rate gradually becomes slower, and the activated carbon still has the adsorption capacity when the solution reaches the equilibrium concentration. According to the adsorption theory, the adsorption effect of activated carbon must be affected by the number of activated carbon micropores during adsorption. During the adsorption process, multiple activated carbon monomers will simultaneously produce adsorption force on a certain particle, so that the interaction between the particles will cancel each other. As the degree of excess increases, more activated carbon adsorbs to the same particle, which further offsets the adsorption competition, and the curve shows a tendency to decrease the velocity gradually.
When the mass of carbon added in the test is 0.1 g, the adsorption amount of coal charcoal is much larger than that of the shell char. According to the literature, the amount of pores and macropores in the activated carbon of the shell is more than that of coal, and the adsorption effect on organic matter. it is good. The results of this test are inconsistent with the literature, and then reappeared in parallel experiments. The analysis suggests that the problem of the test and the texture of the activated carbon of the shell are due to the similar activation time and temperature in the production process of the shell charcoal. Related: The shell charcoal is made by drying, pickling and activating the plant material. Although the mesopores and macropores are distributed more, the adsorption of organic matter is theoretically dominant, but the shell activated carbon has a loose structure and low mechanical strength. In the process of adsorbing organic matter, each activated carbon monomer generates a large number of van der Waals forces which have an influence on adsorption due to the loose structure, and thus the phenomenon that the shell activated carbon has large pores and mesopores developed, but the adsorption effect on organic substances is not good.
The adsorption competition of shell carbon was not strong, but the data was loose and the above analysis was verified. The adsorption of new and old coal-based activated carbon is strong and the index is close. The coal quality of the new charcoal is increased by 0.1 g, and the amount of adsorbed carbon is reduced from the original 325 mg/g to 250 mg/g, which is reduced by 23.1%; The unit adsorption capacity was reduced by 22%. After two years of operation of coal charcoal, the unit adsorption amount does not decrease significantly with the change of mass, and the curve is very similar to the new carbon of coal material. After the adsorption and interception of the activated carbon filter is carried out for a long time, although the pores on the surface of the activated carbon in the filter layer are partially blocked, the interior is still uncontaminated or changed by the influence of pH, and the net adsorption energy remains stable, thereby achieving equilibrium. At the concentration, the force of the organic matter adsorbed in the micropores of the activated carbon maintains the level of the new carbon, and the curve shows that the change trend of the unit adsorption amount is consistent with the new carbon.
4 Conclusion
1 The activated carbon filter material is used to treat the surface water. After two years of continuous operation, the structure and adsorption capacity of the medium and large pores of the coal-based granular activated carbon do not change much.
2 In the micro-polluted surface water environment, the long-term operation has little effect on the 1/n value of the coal-based activated carbon adsorption curve, and basically maintains the adsorption speed of coal-based carbon, which has little effect on the unit adsorption amount of organic matter.
3 Activated carbon microporous adsorption competition has obvious influence on the adsorption of organic matter. With the increase of the mass of activated carbon, its unit adsorption amount is obviously attenuated.
4 Coal-based activated carbon has uniform texture and small impurity content, which can meet the adsorption requirements of organic matter. The adsorption speed of activated carbon of shell is better than that of coal-based activated carbon, but the adsorption amount is small, and the adsorption performance of organic matter is poor. Coal charcoal is suitable for static testing of the Yellow River water treatment in the laboratory, while the larger 1/n value of the shell carbon is more suitable as a biofilter for high-load biofilters.
Interior Wall Paneling,Wooden Wall Coating,Compact Laminat Wall Panel
Fenghua Jade Motor Co., Ltd. , http://www.china-interior-door.com