In breaking through the battery bottleneck, scientists continue to explore various alternative materials, and silicon is recognized by many scientists and is considered a promising material. The scientific research team from Clemson University recently proposed a new design scheme that overcomes some of the problems of incorporating this material into lithium-ion batteries, thus demonstrating a lightweight multi-purpose device that can be used for satellites and Spacesuit power supply.
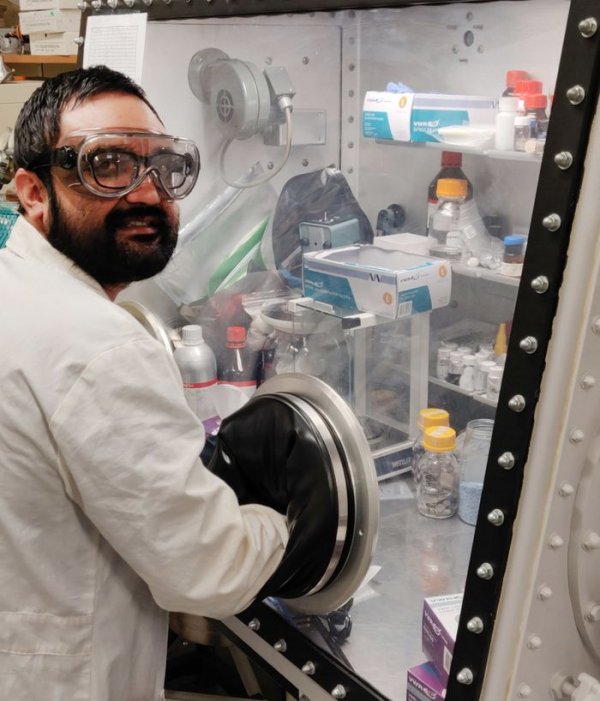
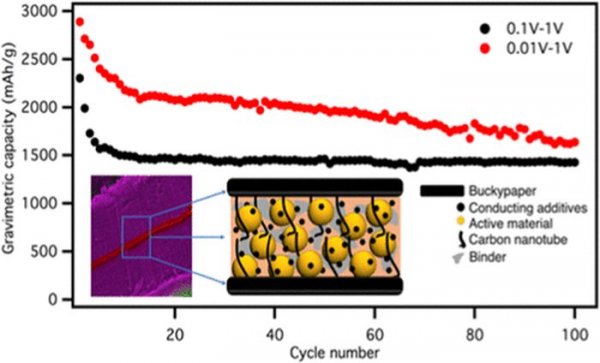

Scientists have long been studying the potential of silicon in lithium-ion batteries. Using this material as an anode component can increase the storage capacity of these devices by 10 times. But to commercialize, some problems need to be solved.
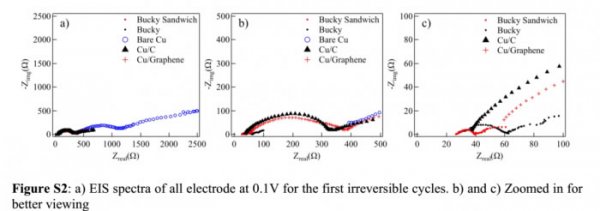
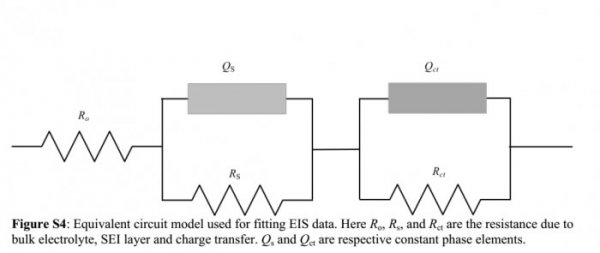
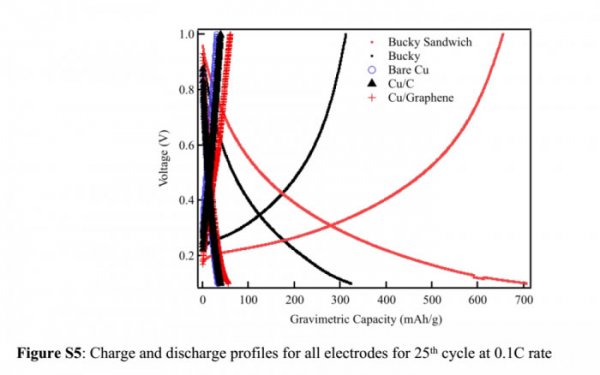
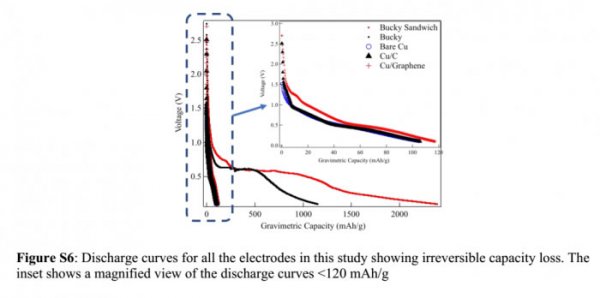
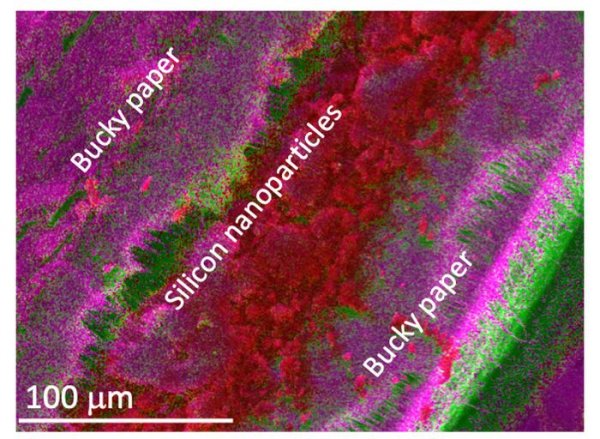
First, silicon does not have the same durability as graphite. When the battery is charged and discharged, it tends to expand, contract and break down into small pieces. This will cause deterioration of the anode and battery failure. In the past few years, scientists have proposed a variety of potential solutions, including the conversion of silicon into sponge-like nanofibers or tiny nanospheres, and then integrating them into devices.
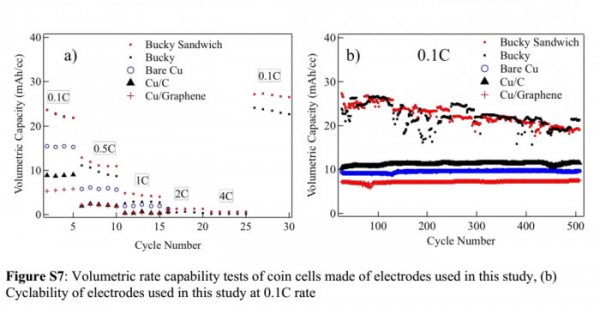
The scientific research team from Clemson University hopes to use the "Buckypaper" carbon nanotube sheet to enhance the reliability of silicon. This carbon nanotube sheet is used to develop the heat shield of the next generation aircraft. These flakes are paired with tiny, nano-scale silicon particles. The team says this arrangement is much like a deck of cards, with silicon particles sandwiched between each layer of cards.
Shailendra Chiluwal, the first author of the study, said: “Independent carbon nanotube sheets maintain electrical connections between silicon nanoparticles. These nanotubes form a quasi-three-dimensional structure. Even after 500 cycles, silicon nanoparticles can be Keep them together and reduce the electrical resistance caused by the nanoparticle rupture."
The team believes that the advantage of this method is that even if the battery's charge and discharge causes the silicon particles to rupture, they are still locked in the interlayer and can perform their functions. This means that in theory, the battery can have a higher capacity, which means that energy can be stored in a lighter battery, thereby reducing the overall weight of the device.
Scientists claim that as an added bonus, the use of nanotubes creates a buffering mechanism that allows the battery to be charged at four times the current iteration rate. This lightweight, high-capacity battery that supports fast charging can be used for many purposes, including electric vehicles, space exploration, and so on.
Research author Ramakrishna Podila said: “Most satellites get their electricity mainly from the sun. But satellites must be able to store energy for them when they are in the shadow of the earth. We must make the batteries as light as possible because the heavier the satellite, the higher the mission cost. ."
The research was published in the journal Applied Materials and Interface.
Portable Wagon Cart:
Portable Wagon Carts use iron or stainless steel frame,covered with durable oxford cloth, can load about 100kg and could be folded when it is not needed, will not spare too much space. This wagon cart is designed as 2 wheels with breaks, then will not move without controlling. Customers could also choose designs with sheds or not.
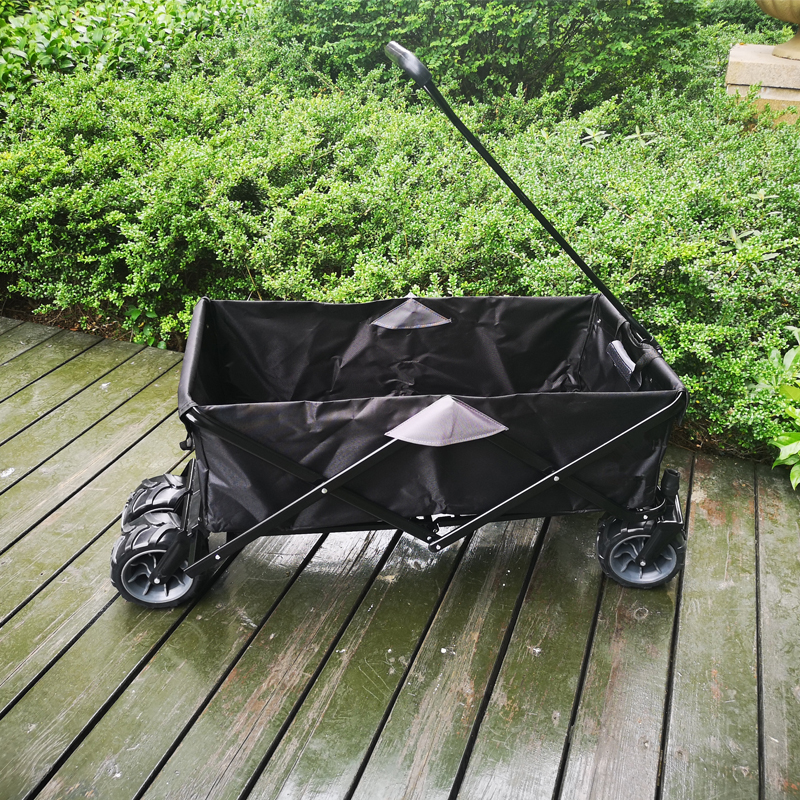

Wagon Beach Cart,Portable Wagon Cart,Foldable Wagon Cart,Foldable Garden Cart,Garden Beach Trolley Cart
Suzhou CoreMission International Trading Co.,Ltd. , https://www.szcoremission.com